Meat, Dairy, and the Planet: Why Veganism is the Future of Sustainability
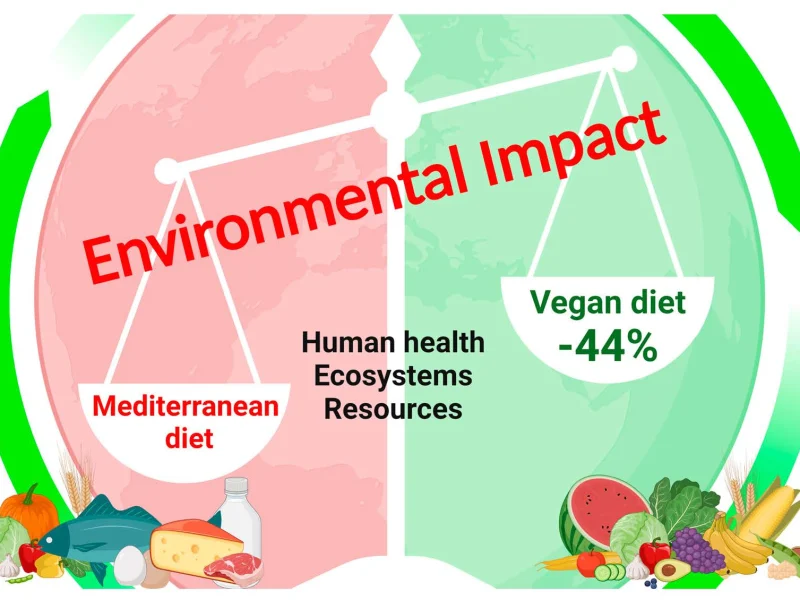
The impact of animal agriculture on the environment is undeniable. From deforestation to greenhouse gas emissions, the production of meat and dairy takes a significant toll on the planet. As the global population grows, so does the demand for food, making it crucial to adopt more sustainable dietary choices. Veganism presents a viable solution to many of the environmental crises we face today.
One of the most alarming consequences of meat and dairy production is deforestation. Large areas of forests, particularly in the Amazon, are cleared to make way for cattle grazing and to grow feed crops like soy and corn. This not only destroys vital ecosystems but also accelerates climate change by releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere.
Water consumption is another pressing issue. Raising animals for food requires immense amounts of water, far more than growing plant-based foods. Producing a single pound of beef can require up to 1,800 gallons of water, while growing an equivalent amount of plant-based protein uses only a fraction of that. With freshwater scarcity becoming a growing concern, shifting towards plant-based eating can significantly reduce our water footprint.
Animal agriculture is also a leading contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. The methane produced by cows is a particularly potent greenhouse gas, with a warming effect many times stronger than carbon dioxide. Moreover, the energy-intensive processes of meat and dairy production, including transportation and refrigeration, further contribute to emissions. A global shift towards plant-based diets could drastically cut greenhouse gas emissions and help mitigate climate change.
The environmental benefits of veganism extend beyond reducing emissions. Industrial farming practices deplete soil nutrients and contribute to pollution through excessive fertilizer and pesticide use. Transitioning to plant-based farming methods, such as regenerative agriculture, can help restore soil health and promote biodiversity.
Some argue that sustainable meat and dairy farming practices can mitigate environmental damage. However, even the most eco-friendly animal farming methods cannot match the sustainability of plant-based food production. The efficiency of growing plants directly for human consumption far outweighs the resource-intensive process of raising animals for food.
Choosing a vegan lifestyle is one of the most impactful steps an individual can take to protect the planet. By reducing our reliance on animal products, we conserve resources, lower emissions, and promote a more sustainable food system for future generations. The future of sustainability lies in rethinking our dietary habits—and veganism is leading the way.